What is Nicotinamide Adenine
Dinucleotide (NAD+)?
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) is one of the most important and interesting molecules in the body. It is required for over 500 enzymatic reactions and plays key roles in the regulation of almost all major biological processes (Ansari and Raghava,2010). Above all, it may allow us to lead healthier and longer lives.1
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)exists in either its oxidized form (NAD+) or reduced form (NADH), which are critical cofactors of a number of oxireductases.
Why is NAD+ important?
NAD+ serves both as a critical coenzyme for enzymes that fuel reduction-oxidation
reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another, and as a cosubstrate for other enzymes as the sirtuins and poly (adenosine diphosphate- -ribose) polymerases. 2. NAD+ Deficiency is a critical common pathological factor in a number of diseases.3.
Therapeutic interventions by the administration of NMN, NAD+, or recombinant NAMPT are effective for restoring adult neurogenesis in several neurological diseases.4
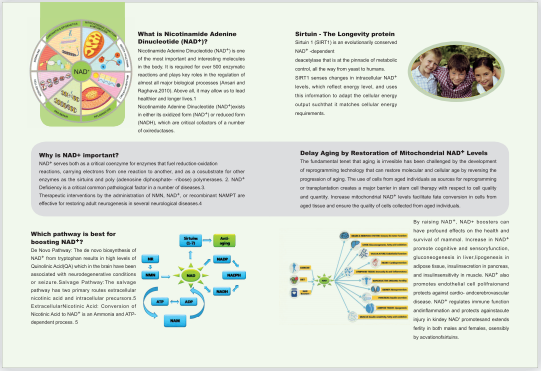
Which pathway is best for boosting NAD+?
De Novo Pathway: The de novo biosynthesis of NAD+ from tryptophan results in high levels of Quinolinic Acid(QA) which in the brain have been associated with neurodegenerative conditions or seizure.Salvage Pathway:The salvage pathway has two primary routes extracellular nicotinic acid and intracellular precursors.5 ExtracellularNicotinic Acid: Conversion of Nicotinic Acid to NAD+ is an Ammonia and ATP-dependent process. 5
Sirtuin - The Longevity protein
Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) is an evolutionarily conserved NAD+ -dependent
deacetylase that is at the pinnacle of metabolic control, all the way from yeast to humans.
SIRT1 senses changes in intracellular NAD+ levels, which reflect energy level, and uses this information to adapt the cellular energy output suchthat it matches cellular energy requirements.
Delay Aging by Restoration of Mitochondrial NAD+ Levels
The fundamental tenet that aging is irrvesible has been challenged by the development of reprogramming technology that can restore molecular and cellular age by reversing the progression of aging. The use of cells from aged individuals as sources for reprogramming or transplantation creates a major barrier in stem cell therapy with respect to cell quality and quantity. Increase mitochondrial NAD+ levels facilitate fate conversion in cells from aged tissue and ensure the quality of cells collected from aged individuals.
By raising NAD+, NAD+ boosters can have profound effects on the health and survival of mammal. Increase in NAD+ promote cognitive and sensoryfunction, gluconeogenesis in liver,lipogenesis in adipose tissue, insulinsecretion in pancreas, and insulinsensitivity in muscle. NAD+ also promotes endothelial cell polifraionand protects against cardio- andcerebrovascular disease. NAD+ regulates immune function andinflammation and protects againstacute injury in kindey NAD' promotesand extends ferlity in both males and females, osensibly by acvationofsirtuins.
NAD+
A reliable supplier
PURE » 98% NAD
PRODUCTION Made under GMPA
PPEARANCE off- white, odorless
Studies of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide ( NAD+ )
NAD+ was originally discovered by Harden and Young in 1906 as a factor that couldenhance the rate of fermentation in yeast extracts. Over Subsequent years, research onthe biology of NAD+ has been gaining momentum, providing many critical insights intothe pathogenesis of age- associated functional decline and diseases

Study Title
NAD*controls neural stem cell fate in the aging brain
Restoration of Mitochondrial NAD+ Levels Delays
Stem Cell Senescence and Facilitates Reprogramming
of Aged Somatic Cells
Targeting Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyl transferase
as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Restore Adult
Neurogenesis
SIRT2 induces the check point kinase Bubr1 to
increase lifespan
Nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuates brain injury
after intracerebral hemorrhage by activating
Nrf2/Ho-1 signaling pathway
Chronic Nicotinamide Riboside supplementation is
well-tolerated and elevates NAD+ in healthy middle
aged and older adults
Declining NAD+ Induces a Pseudohypoxicstate
Disrupting Nuclear-mitochondrial Communication
during Aging
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, a Key NAD+
Intermediate, Treats the Pathophysiology of Diet-and
Age-induced Diabetes in Mice
Research Institution
Buck Institute for Research on Aging.
Novato. CA USA
National Research Foundation of Korea Ministry of Science, IC T and Future Planning and KRIBB/KRCF research initiative program, Korea
National Natural Science Foundation of China
Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA USA
Department of Pharmacology, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, China
Martens C R, Denman B A, Mazzo M R, et al
Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA USA
Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO, USA
DOI#
10.15252/embj.2014
88969
10.1002/stem.2460
10.1111/cns.12539
10.15252/emgj.2013
86907
10.1038/s41598-
017-00851-z
Nature
communications,
2018,9(1):1286.
Cell,2013,
155(7):1624-38
Cell Metabolism,
2016,24(6):795
What is Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, reduced form (NADH)?
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) exists in either its oxidized form (NAD+) orreduced form (NADH), which are critical cofactors of a number of oxireductases.
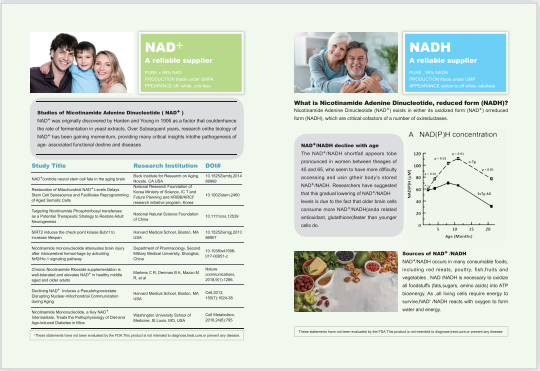
NAD+/NADH decline with age
The NAD+/NADH shortfall appears tobe pronounced in women between theages of 45 and 65, who seem to have more difficulty accessing and usin gtheir body's stored NAD+/NADH. Researchers have suggested that this gradual lowering of NAD+/NADH
levels is due to the fact that older brain cells consume more NAD+/NADH(anda related antioxidant, glutathione)faster than younger cells do.
Sources of NAD+ /NADH
NAD+/NADH occurs in many consumable foods, including red meats, poultry, fish,fruits and vegetables . NAD /NADH is necessary to oxidize all foodstuffs (fats,
sugars, amino acids) into ATP bioenergy. As ,all living cells require energy to survive,NAD' /NADH reacts with oxygen to form water and energy.
These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA.This product is not intended to diagnose,treat,cure,or prevent any disease.
